Working in the laboratory may include handling hazardous samples such as chemicals, microorganisms, and drug compounds— all of which pose a threat to human health and the environment. An airflow containment equipment provides operator and sample protection from hazards by means of calculated airflow velocity, airflow direction, and filtration system. To guarantee optimum performance, it is vital to have these cabinets installed in proper location sites.
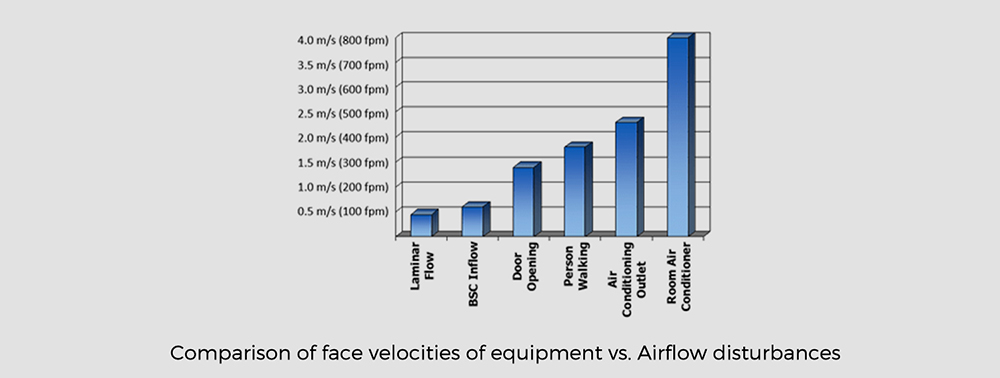
Due to the low face velocity of the cabinets, external airflow disturbances such as a door opening, a person walking, an air conditioner, or a fan can cause disruption and turbulence inside the cabinet’s work zone. Therefore, these cabinets must be installed or positioned in a way that optimally protects the airflow.
Protect the airflow! Follow these tips for the proper location of your containment devices.
1.If possible, an initial site assessment must be done. This will provide an overview of the facility’s available space and will enable the engineers to plan for the installation and placement of the cabinets.
2.Cabinets should never be placed in line with a doorway or a window that can be opened.
3.Ensure that there are no room air diffusers, fans, extractors, or vents, placed directly towards the opening of the Biological Safety Cabinets, Laminar Flow Cabinets, and Fume Hoods.
4.The position of the cabinet should satisfy the spatial requirements (e.g., vision, lighting, and convenience of access) of the operator and people working nearby.
Position Requirements
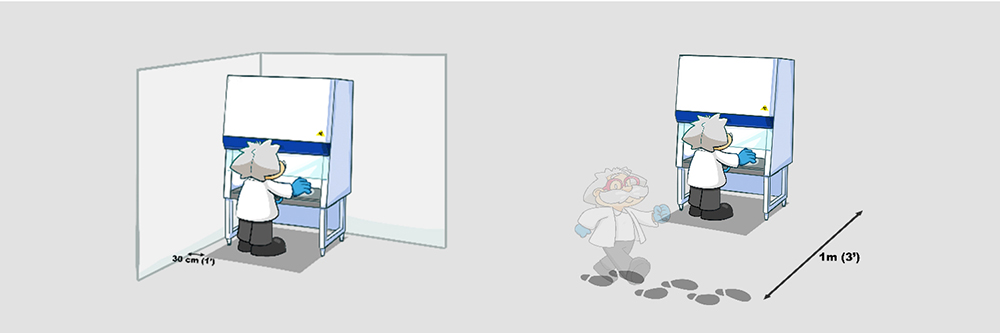
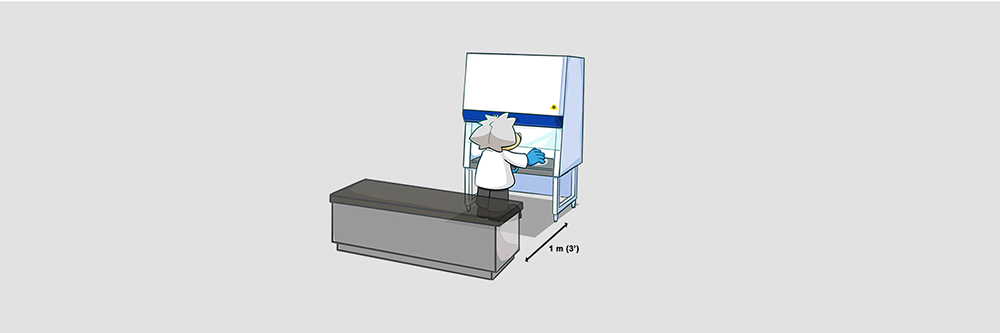
Allow at least 1.0-meter (3’) clearance from the front of the cabinet to any pedestrian traffic routes, thoroughfares, or walkways.
Allow at least 30 cm (1’) clearance on both sides of the cabinet. There should be adequate space left for cleaning the sides of the cabinet and for carrying out decontamination procedures. There should be unobstructed access to the main power supply point(s).
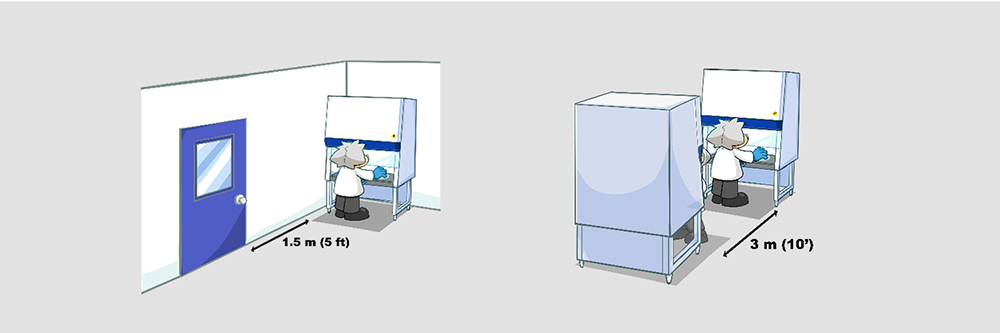
Do not position the cabinet where the distance between the aperture and any doorway is less than 1.5 meters (5’) or the distance between the side panel and any doorway is less than 1.0 meter (3’). Door openings cause substantial air turbulence. If the door is fitted with air transfer grills, operator protection factor testing may be carried out to determine suitable reduced clearance.
Safety cabinets should not be installed in positions where there is a likelihood of interference from other laboratory equipment. The distance from the aperture to the aperture of an opposing cabinet, fume cupboard, etc. should be more than 3 meters (10’) for safe operation.
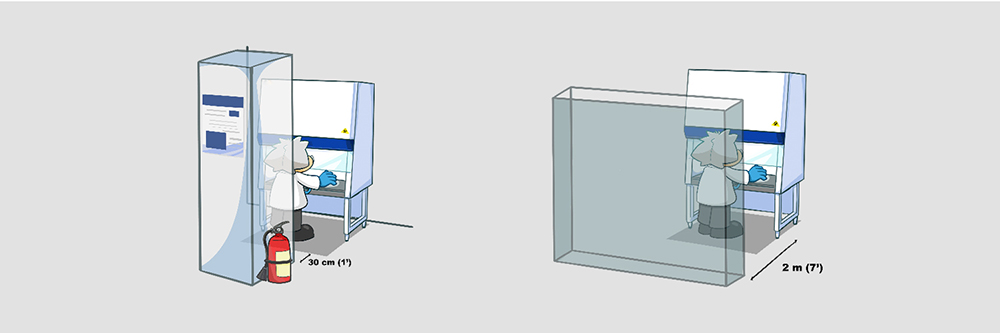
As with walls, any large obstruction such as a pillar or column projecting beyond the plane of the front aperture should not be within 30 cm (1’) of the sides of the cabinet.
Do not position the cabinet in a location where there is an opposing wall (or other obstruction likely to affect airflow) within 2 meters (7’) of the front aperture.
A projecting bench will help minimize traffic in front of the cabinet and anyone working at the bench is unlikely to have a significant effect on the airflow if the front of the bench is situated at least 1 meter (3’) from the side of the cabinet.
Exhaust Requirements
A clearance of at least 30 cm (1’) is recommended between the highest point of the cabinet and the ceiling. If the distance is less than 30 cm (1’), the airflow alarm system may need re-calibration.
For proper exhaust filter leak scanning purposes, a minimum clearance of 50 cm is recommended.
Post time: Jul-07-2022